Material Data Sheet
Heritage Sour Service - SM-80S
SM-80S is a low alloy Carbon steel OCTG material suitable for severe Sour Service applications. SM-80S is a Sulfide Stress Cracking (SSC) resistant material.
SSC failure mechanism is a form of Hydrogen embrittlement in combined presence of H2S, water and tensile stresses. SM-80S benefits from SMI’s unrivaled know-how in manufacturing sour service materials since the 70’s and best-in-class quality control. SM-80S offers a tighter quality control compared to API L80 and is manufactured based on API 5CT/ISO 11960 PSL2 requirements.
Diameters: 2-3/8” to 16”
Weights: as per API 5CT/ISO 11960
Special application: Please contact Nippon Steel engineer, should You require specific size, weight, drift, or any other characterization.
- Proprietary SM-S series.TGP-2840 (latest revision)
- API 5CT / ISO 11960
- NACE MR0175 / ISO 15156-2
- API 5C1 / ISO 10405
- NACE TM0177
- VAM Book
Severe Sour service application corresponding to region 3, High H2S combined with low pH, as defined by NACE MR0175/ISO15156-2 (Fig 1) :
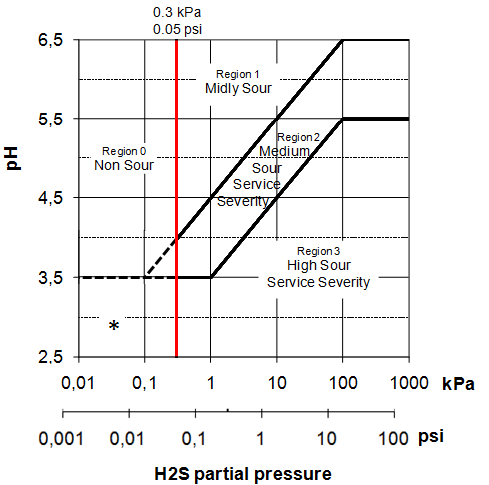
Fig. 1 : Sour Service regions in the pH vs H2S diagram
* Note : Even though this low pH corner is considered non-sour as far as H2S is concerned, caution needs to be exercised, as High Strength materials may become susceptible to Environmental Cracking (EC) even with no or very limited H2S.
For each manufactured SM-80S heat, SSC resistance is verified through testing in accordance with NACE TM0177 method A, in solution A, using an applied stress of 90% SMYS while API L80 is delivered without SSC testing.
As an option SM-80S can be supplied with NACE TM0177 method D testing.
SM80S is a low alloy sour service material; consequently SM80S can be susceptible to metal loss corrosion if exposed to a wet dynamic acid gas containing environment, such as CO2.
For a more detailed assessment please contact Nippon Steel engineers.
| PROCESS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Steel making | Ladle refined, fully killed and vacuum degassed; continuously cast to a fine grained practice |
| Pipe making | Seamless |
| Heat treatment | Quenched and Tempered |
| YIELD STRENGTH KSI |
TENSILE STRENGTH KSI |
ELONGATION % |
HARDNESS HRC |
TECHNICAL NOTE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Min | Min | Max | |
| 80 | 95 | 95 | API Formula | 23.0 | 90% SMYS 1bar H2S, NACE A, Solution-A |
| UNIT | 25°C | 50°C | 100°C | 150°C | 200°C | 250°C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density | Kg/m3 | 7800 | 7790 | 7780 | 7760 | 7750 | 7730 |
| Young's modulus | GPa | 213 | 211 | 209 | 206 | 203 | 200 |
| Poisson's Ratio | - | 0.30 | 0.29 | 0.29 | 0.29 | 0.29 | 0.28 |
| Tensile strength de-rating | % | 100 | 98.3 | 95.5 | 94.4 | 94.7 | 94.7 |
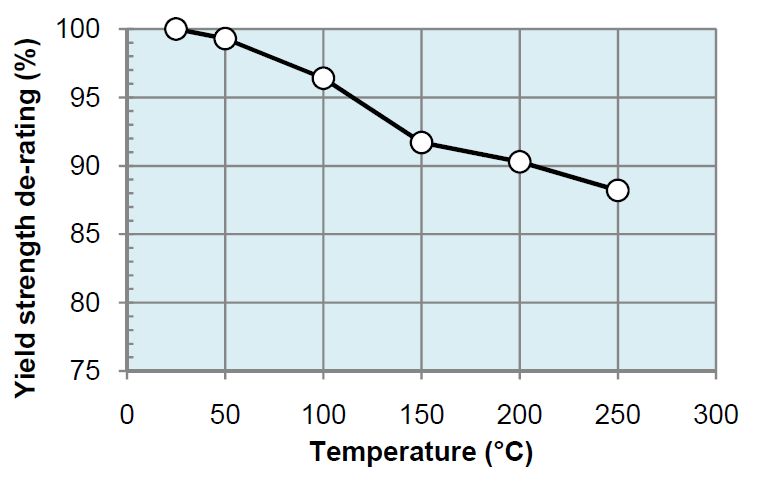
| Yield strength de-rating | % | 100 | 99.3 | 96.4 | 91.7 | 90.3 | 88.2 |
| Thermal Diffusivity | x10-6 m2/s | 12.3 | 12.3 | 11.9 | 11.3 | 10.6 | 9.96 |
| Heat Capacity | x106 J/m3 deg.C | 3.61 | 3.79 | 3.83 | 3.97 | 4.15 | 4.34 |
| Thermal Conductivity | W/m deg.C | 44.4 | 46.7 | 45.6 | 44.8 | 44.0 | 43.3 |
| Specific Heat | J/Kg deg.C | 463 | 487 | 492 | 511 | 535 | 562 |
| Thermal expansion | x10-6 / deg.C | - | 12.5 | 12.4 | 12.6 | 12.8 | 13.0 |
While the increase of temperature minimizes SSC susceptibility as outlined in Figure 2, SM-80S remains SSC resistant at all temperatures.
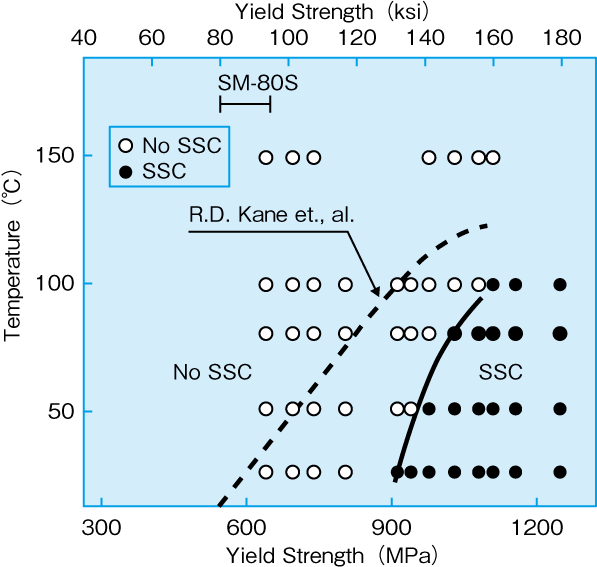
Fig. 2 : Dependency of SSC susceptibility on test temperature.
SMI modified 4130 material,σappl=100%AYS, pH2S=100kPa at 25 deg.C, NACE Method A, solution A.
[Ref : R.D.Kane et,.al.J.Petroleum Technology, 1483(1977)]
In addition, Figures 2 features the major sensitivity of SSC resistance to the material strength : SSC susceptibility increases along with material Yield strength. On that regards, SM-80S preserves its SSC resistance across the full range of its specified Yield strength range, as shown in Figure 3.
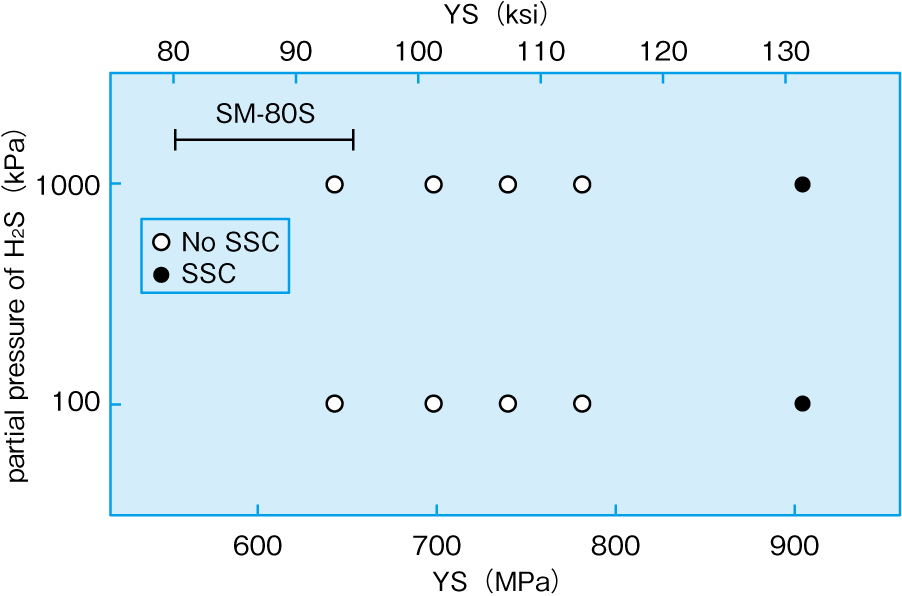
Fig. 3 : H2S partial pressure versus materials SSC behavior.
SMI modified 4130 material, σappl=100%AYS, 4PB, solution A, 25 deg.C.
While NACE TM0177 has standardized its testing environment to 100kPa H2S, Nippon Steel has explored SSC susceptibility at higher H2S partial pressure, as illustrated in Figure 3, in order to assess the robustness of its material designs and processes. SM-80S was successfully tested up to 1000 kPa or 10 bar H2S, and is to be considered full fledge Sour Service.
For additional information about material performances please contact Nippon Steel engineers.
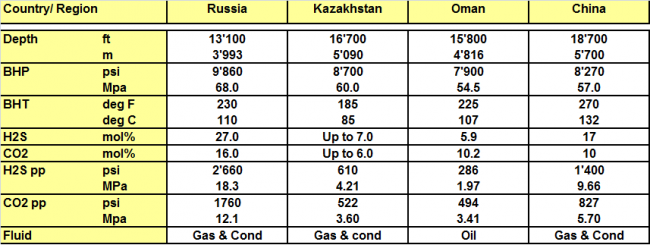
A selection of critical applications of Sumitomo Sour Service proprietary grades shows the extensive record in region 3. These Field records include SM-80S, SM-90S and SM-95S used as intermediate, production casing and tubing. More detailed well conditions are provided below along with the specified material :
Health, Safety and Environment
While state-of-the-art HSE rules are applied throughout Nippon Steel manufacturing process, proprietary and specific HSE regulations shall be applied along the life cycle of the pipe until it reaches its final position in the well, according to each operator’s rules. This particularly applies to all phases of handling and transportation, assembly on the rig floor, and rig return if applicable. OCTG are heavy and by nature unstable. Special care shall be paid to potential risks of injury whenever handling OCTGs. Walking on pipes shall be avoided at all times. Usage of Personal Protection Equipments (PPE) is mandatory. Equipment and procedures will be established to capture the possible wastes generated during maintenance (cleaning, coating, doping) and disposed according to local regulations. This applies in particular to storage dope, running dope, or cleaning water wastes.
Best practices for transportation, handling and storage of OCTG in general are covered by ISO 10405 / API RP5C1. VAM Book is also a good source of handling practices for VAM connections. In addition to these general rules, specific care is recommended pertaining to SM-S series, because improper handling could affect the material performances and by extension the corrosion resistance :
- Prevention of Spot Hardening
For more specific information please contact Nippon Steel engineers.