Material Data Sheet
Nickel Alloy - SM2550-125
SM2550 is an Austenitic Ni base material required for critical well conditions combining high concentrations of CO2, H2S and Chlorides that was launched in the mid-80’s by Nippon Steel for Tubing & Liner applications in severe environments. It benefits from Nippon Steel’s unrivaled know-how in manufacturing CRA (Corrosion Resistance Alloys) materials and best-in-class quality control.
SM2550 is manufactured based on API 5CT / ISO 11960 and API 5CRA / ISO 13680
Diameters: 2 3/8” to 7 5/8” (larger sizes can be available upon request)
Weights: as per API 5CT/ISO 13680. Please note that while the API 5CT/ISO 11960 linear weight will define the pipe wall thickness the actual linear weight of the material will be slightly greater due to the heavier density of the elements it contains versus carbon steel.
Special application: Please contact Nippon Steel engineer, should you require specific size, weight, drift, or any other characterization.
- Proprietary SM2550 series. TGP-0798 (latest revision)
- API 5CT / ISO11960
- NACE MR0175 / ISO 15156
- API RP 5C1 / ISO 10405
- API 5CRA / ISO 13680
- VAM Book
- Nippon Steel Storage and handling procedure for CRA materials
Corrosive environments featuring the combined presence of CO2 + H2S + Chloride, in temperatures up to 177 °C, in absence of elemental Sulfur
Its primary function is Tubing and Liner, sections permanently exposed to production fluids
Final material application will depend upon CO2, H2S, Temperature, pH and expected Chlorides content. For a more detailed assessment please contact Nippon Steel engineers.
| PROCESS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Steel making | Steel shall be made by electric furnace process followed by Vacuum Oxygen Decarburization (VOD) process &/or Argon Oxygen Decarburization (AOD) Process |
| Pipe making | Manufactured through Cold working the hot formed tubular product and shall be furnished in a cold worked conditions |
| Heat treatment | Solution Annealing Process before final cold drawing |
(mass %)
| C | Si | Mn | Cu | Ni | Cr | Mo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤ 0.03 | ≤ 1.00 | ≤ 1.00 | ≤ 1.20 | 47.0 ~ 52.0 | 23.0 ~ 26.0 | 6.0 ~ 9.0 |
UNS Number: N06255
| YIELD STRENGTH KSI |
TENSILE STRENGTH KSI |
ELONGATION % |
HARDNESS HRC |
TECHNICAL NOTE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Min | Min | Max | |
| 125 | 145 | 130 | 13 | 36.0 | - |
| UNIT | 25°C | 100°C | 150°C | 200°C | 250°C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density | Kg/m3 | 8220 | 8200 | 8180 | 8160 | 8140 |
| Young's modulus | GPa | 196 | 193 | 191 | 189 | 188 |
| Poisson's Ratio | - | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 |
| Tensile strength de-rating | % | 100.0 | 95.1 | 92.5 | 90.7 | 87.8 |
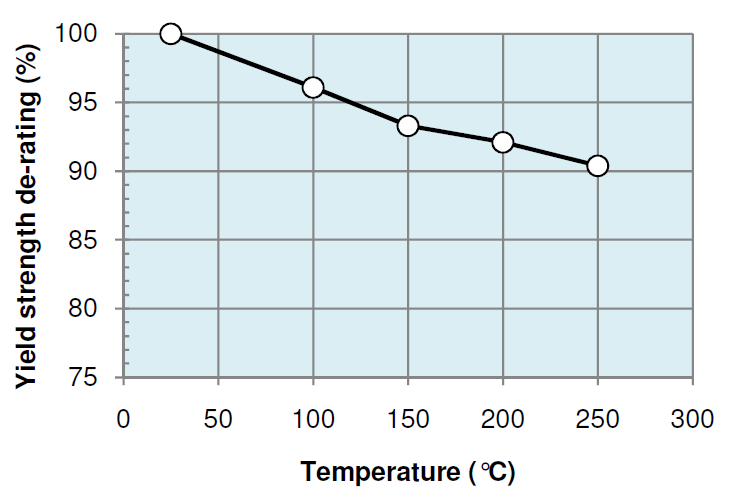
| Yield strength de-rating | % | 100.0 | 96.1 | 93.3 | 92.1 | 90.4 |
| Thermal Diffusivity | x10-6 m2/s | 2.83 | 3.16 | 3.40 | 3.51 | 3.74 |
| Heat Capacity | x106 J/m3 deg.C | 3.18 | 3.35 | 3.45 | 3.53 | 3.63 |
| Thermal Conductivity | W/m deg.C | 9.0 | 10.6 | 11.7 | 12.4 | 13.6 |
| Specific Heat | J/Kg deg.C | 387 | 409 | 422 | 433 | 446 |
| Thermal expansion | x10-6 / deg.C | - | 13.1 | 13.4 | 13.5 | 13.6 |
* Data will be shortly available.
In wet combined CO2 & H2S environments, for temperatures exceeding 149°C (300°F) usage of SM2550 is recommendable starting from H2S partial pressure exceeding 0.1 bar:
- for lower H2S partial pressure ranging between 0.1 to 1.0 bar, these materials should be considered depending upon the combination of critical variables such as pH, Chloride content, S0 and temperature.
- for H2S partial pressures exceeding 1.0 bar the only metallurgical solution to counter corrosion is to consider Austenitic Fe base or Nickel base materials.
Since H2S is a potent pitting agent, a passivation film composed of Ni-S, Cr-O & Mo-S is required to maintain stability and protect the bulk material from corrosion attack up to a defined temperature threshold in wet combined CO2 & H2S environment. This is achieved through alloying of Cr-Ni & Mo.
SM2550 is a nominal 6% Molybdenum material recognized by ISO-13680 as Group 4 Category 25-50-6. This material is referenced as 4d material in NACE MR0175 /ISO 15156-3 (please refer to Fig. 1).
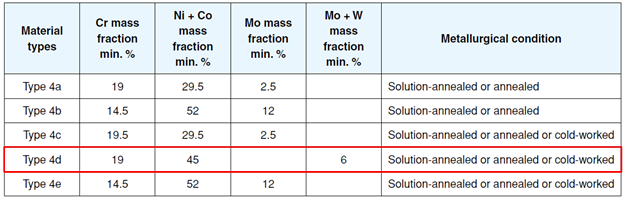
Fig 1: NACE MR0175 / ISO 15156-3 2003 Table A12
For this type of material, NACE MR0175 /ISO 15156-3 indicate the following application limits as general guidelines :
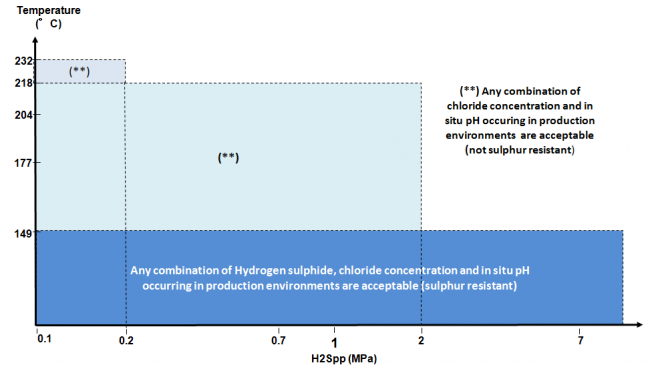
Fig 2: Material 4d application boundaries per NACE MR0175 / ISO 15156-3 2003 (Ref. Table A-14)
According to NACE MR0175 / ISO 15156-3 2003, final material selection for the intended service will be equipment user’s responsibility and detailed information exchange with manufacturer is highly recommendable.
Nippon Steel, in absence of elemental sulfur, recommends usage of SM2550 materials for temperature up to 177°C (350°F) higher than 149°C (300°F) limit specified by ISO 15156-3.
This difference is based on Nippon Steel’s unrivaled know-how in manufacturing austenitic stainless steel since the mid 80’s and best-in-class quality control.
For fit for purpose conditions (** in Fig 2), Nippon Steel proposes verification test under the actual field condition.
Fig 3 below represents Nippon Steel SCC limits on various Austenitic materials.
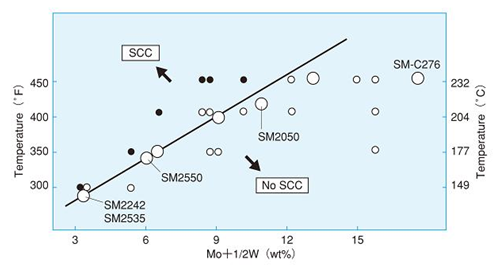
Fig. 3: Relation between testing temperature and Mo content of Nickel Alloy in
H2S- Cl- environment in SSRT (25% NaCl+ CH3COOH, 0.7 MPa (100 psi) H2S)
For additional information about material performances please contact Nippon Steel engineers.
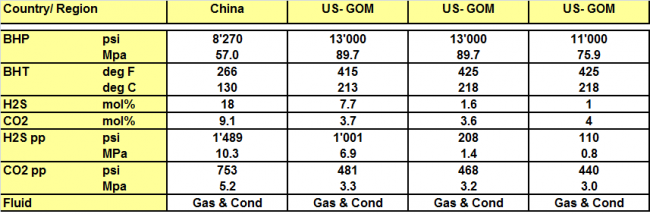
A selection of critical applications of SM2550 is shown below. These Field records include SM2550 material used as Tubing and Liner.
While state-of-the-art HSE rules are applied throughout Nippon Steel manufacturing process, proprietary and specific HSE regulations shall be applied along the life cycle of the pipe until it reaches its final position in the well, according to each operator’s rules. This particularly applies to all phases of handling and transportation, assembly on the rig floor, and rig return if applicable. OCTG are heavy and by nature unstable. Special care shall be paid to potential risks of injury whenever handling OCTGs. Walking on pipes shall be avoided at all times. Usage of Personal Protection Equipments (PPE) is mandatory. Equipment and procedures will be established to capture the possible wastes generated during maintenance (cleaning, coating, doping) and disposed according to local regulations. This applies in particular to storage dope, running dope, or cleaning water wastes.
Best practices for transportation, handling and storage of OCTG in general are covered by ISO 10405 / API RP5C1. VAM Book is also a good source of handling practices for VAM connections. In addition to these general rules, specific care is recommended pertaining to SM-2550, because improper handling could affect the material performances and by extension the corrosion resistance :
- Prevention of Spot Hardening
- Prevention of Iron contamination
- Adapted running equipments and practices
- Prevention of corrosion on rig returns, particularly in presence of completion fluids
For more specific information please refer to Nippon Steel Storage and handling procedure for CRA materials or contact Nippon Steel engineers.