Material Data Sheet
Duplex Stainless Steel - SM25CRW-125

SM25CRW is a Duplex Stainless Steel material, generically called Super Duplex because its PREN value exceeding 40. SM25CRW is used in corrosive well conditions in combined presence of CO2, low H2S and Chlorides. Launched in the early 90’s, SM25CRW benefits from Nippon Steel’s unrivaled know-how in manufacturing CRA (Corrosion Resistance Alloys) materials and best-in-class quality control.
SM25CRW-125 is manufactured based on API 5CT / ISO 11960 and API 5CRA / ISO 13680.
Diameters: 2 3/8” to 7 5/8” (larger sizes can be available upon request)
Weights: as per API 5CT/ISO 13680.
Special application: Please contact Nippon Steel engineer, should you require specific size, weight, drift, or any other characterization.
- Proprietary SM25CRW series. TGP-3707 (latest revision)
- API 5CT / ISO11960
- NACE MR0175 / ISO 15156
- API RP 5C1 / ISO 10405
- API 5CRA / ISO 13680
- VAM Book
- Nippon Steel Storage and handling procedure for CRA materials
Corrosive production environments featuring combined presence of CO2 + low H2S + Chlorides.
Water injection environments featuring presence of dissolved oxygen.
Its primary function is Tubing and Liner, sections permanently exposed to production/injection fluids
In production environments, SM25CRW is typically fit for deep, HP-HT applications requiring high strength materials where localized corrosion is a major concern (high temperature, high chlorides and low pH).
Final material application in production environments will be driven by CO2, H2S, Temperature, pH and expected Chlorides content.
Another typical application of SM25CRW material is for water handling systems where presence of dissolved O2 is expected. In this case, a clear definition of the dissolved oxygen content (O2) and/or presence of free Chlorine will be needed to ascertain SM25CRW suitability function of the anticipated service temperature.
In addition, compatibility with packer & completion fluids (brines and additives), matrix acidizing fluids, and scale dissolvers need to be ascertained.
For a more detailed assessment please contact Nippon Steel engineers.
| PROCESS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Steel making | Steel shall be made by electric furnace process or blast furnace followed by Vacuum Oxygen Decarburization (VOD) process &/or Argon Oxygen Decarburization (AOD) Process |
| Pipe making | Manufactured through Cold working the hot formed tubular product – Final product shall be furnished in cold worked condition |
| Heat treatment | Solution Annealing Process before final cold drawing |
(mass %)
| C | Si | Mn | Cu | Ni | Cr | Mo | W | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤ 0.03 | ≤ 0.80 | ≤ 1.00 | 0.2 ~ 0.8 | 6.0 ~ 8.0 | 24.0 ~ 26.0 | 2.5 ~ 3.5 | 1.5 ~ 2.5 | 0.24 ~ 0.32 |
UNS Number: S39274
| YIELD STRENGTH KSI |
TENSILE STRENGTH KSI |
ELONGATION % |
HARDNESS HRC |
TECHNICAL NOTE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Min | Min | Max | |
| 125 | 145 | 130 | 11 | 37.0 | - |
| UNIT | 25°C | 100°C | 150°C | 200°C | 250°C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density | Kg/m3 | 7890 | 7870 | 7850 | 7830 | 7820 |
| Young's modulus | GPa | 197 | 193 | 190 | 186 | 183 |
| Poisson's Ratio | - | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 |
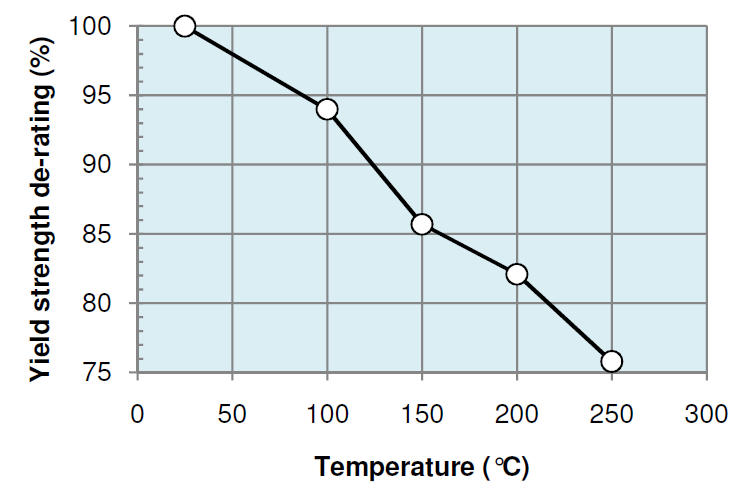
| Tensile strength de-rating | % | 100.0 | 92.3 | 85.2 | 83.1 | 79.8 |
| Yield strength de-rating | % | 100.0 | 94.0 | 85.7 | 82.1 | 75.8 |
| Thermal Diffusivity | x10-6 m2/s | 3.41 | 3.75 | 3.80 | 3.92 | 4.05 |
| Heat Capacity | x106 J/m3 deg.C | 3.14 | 3.27 | 3.40 | 3.48 | 3.66 |
| Thermal Conductivity | W/m deg.C | 10.7 | 12.3 | 12.9 | 13.7 | 14.8 |
| Specific Heat | J/Kg deg.C | 398 | 416 | 433 | 445 | 468 |
| Thermal expansion | x10-6 / deg.C | - | 13.1 | 13.1 | 13.4 | 13.6 |
* Data will be shortly available.
In wet CO2 environments, one of the main limitations of Martensitic Stainless Steels (either as API L80-13CR or any enhanced version like SM13CRS) are:
- SSC (Sulfide Stress Cracking) resistance in presence of H2S
- SCC (Stress Corrosion Cracking) resistance in combined presence of H2S and Chlorides.
In low content H2S environments, Duplex materials exceed martensitic stainless steel corrosion resistance (specifically localized corrosion) following the chemistry logic where increase of elements such as Cr, Mo and W provides a more stable spontaneous passive film developed by the material when exposed to a corrosive environment.
The duplex terminology comes from the material dual micro structure composed of approximately 50% Ferrite and 50% Austenite. The intention in using this dual structure is to maintain the same pitting index in the ferrite and austenite phases, while keeping a high Yield strength in solution treated condition, as illustrated in the PREN formula:
PREN = Cr + 3.3(Mo+0.5W) + 16N (in mass%)
SM25CRW falls into the generic category of the “Super Duplex” which also means that the pitting index, PREN exceeds 40. SM25CRW is recognized by ISO-13680 as Group 2 Category 25-7-4.
NACE MR0175/ISO15156’s stance concerning Super Duplex materials is as follows:
For duplex material with 40<PREN <45 :
Maximum applicable H2S is 3.0 psi (20 kPa) with any combinations of temperature and pH (in producing environment). Chlorides are restricted to 120 kppm.
Nippon Steel’s position toward SM25CRW SCC resistance is more comprehensive, where the material capability to withstand higher H2S partial pressure will be inversely proportional to the expected Chlorides content (See Fig 1).
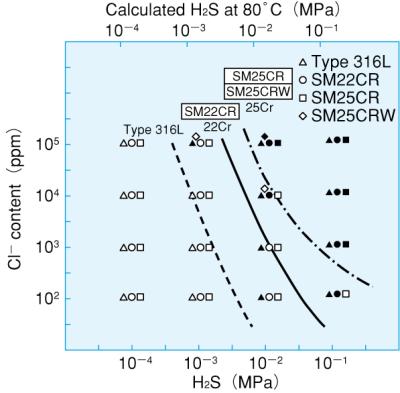
Fig 1: Duplex & Super Duplex Chlorides and H2S limitation
Open: No SCC, Solid: SCC
It is worth noting that the SSC susceptibility of duplex materials is the highest between 80 to 100°C. This, in contrary to C-steel, low alloy materials or martensitic type of steel where SSC is a low/ambient temperature problem which explains why 80°C was selected to conduct SSRT test as illustrated in Figure 1 and 2.
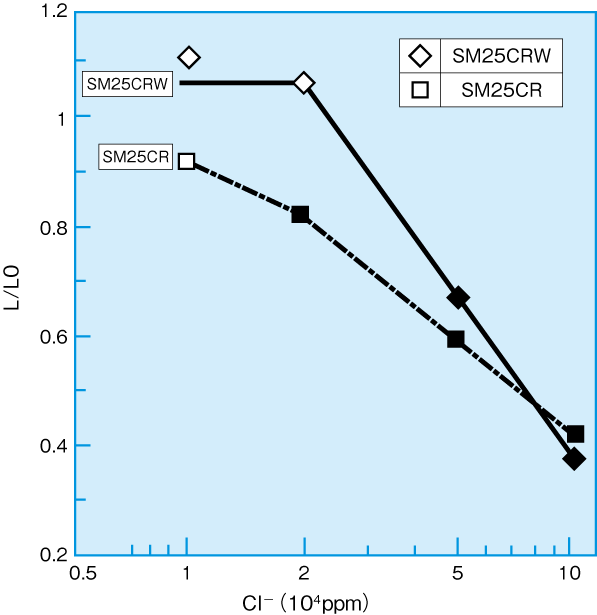
Fig 2:SCC susceptibility of Duplex & Super Duplex steel in Cl- - H2S environments.
(SSRT method; 80°C, Calculated H2S 15kPa, strain rate 4.2 x 10-6/s )
Open: No SCC, Solid: SCC
Figure 2 illustrates SM25CRW improved SCC resistance versus SM25CR material as a function of H2S partial pressure and Chloride content.
As mentioned before another typical application where SM25CRW has been typically used is for water handling systems (water injection, WAG wells) where presence of dissolved O2 is expected. In this case the generic application limits of the material are determined by the material CPT (Critical Pitting Temperature):
Oxygen > 20 ppb :
-
If no chlorination treatment is used: SM25CRW can be used for temperatures < 60°C
-
If chlorination treatment is used: SM25CRW can be used for temperatures < 20°C
For additional information about material performances please contact Nippon Steel engineers.
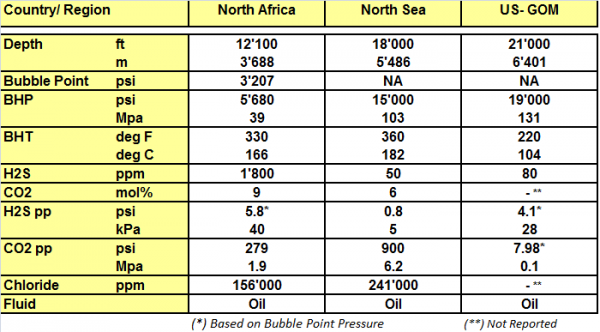
A selection of critical applications of SM25CRW is shown below. These Field records include SM25CRW material used as Tubing and Liner.
While state-of-the-art HSE rules are applied throughout Nippon Steel manufacturing process, proprietary and specific HSE regulations shall be applied along the life cycle of the pipe until it reaches its final position in the well, according to each operator’s rules. This particularly applies to all phases of handling and transportation, assembly on the rig floor, and rig return if applicable. OCTG are heavy and by nature unstable. Special care shall be paid to potential risks of injury whenever handling OCTGs. Walking on pipes shall be avoided at all times. Usage of Personal Protection Equipments (PPE) is mandatory. Equipment and procedures will be established to capture the possible wastes generated during maintenance (cleaning, coating, doping) and disposed according to local regulations. This applies in particular to storage dope, running dope, or cleaning water wastes.
Best practices for transportation, handling and storage of OCTG in general are covered by ISO 10405 / API RP5C1. VAM Book is also a good source of handling practices for VAM connections. In addition to these general rules, specific care is recommended pertaining to SM25CRW, because improper handling could affect the material performances and by extension the corrosion resistance :
- Prevention of Spot Hardening
- Prevention of Iron contamination
- Adapted running equipments and practices
- Prevention of corrosion on rig returns, particularly in presence of completion fluids
For more specific information please refer to Nippon Steel Storage and handling procedure for CRA materials or contact Nippon Steel engineers.